An income tax is a tax imposed on individuals or entities on the incomes earned by them. Every country has its own tax rules, acts, and guidelines. However, it is generally calculated as a percentage of total taxable income. In this article, we shall discuss income tax in India, Singapore and Dubai.
Table of Contents
Income tax in Singapore
Income tax rates depend upon the residential status of the person. There are different tax rates for a person resident of Singapore and a person non resident of Singapore.
Let us clearly understand this.
Individual
Residential Status
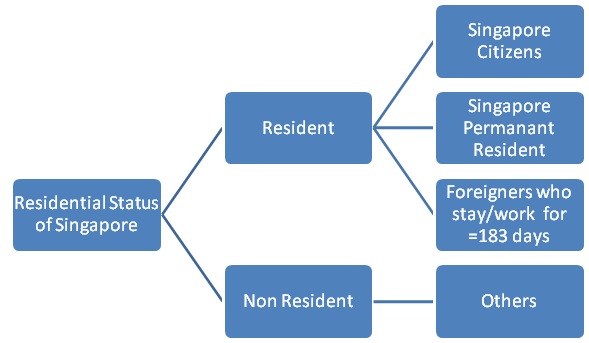
Resident
- Singapore Citizens – Normally resides in Singapore except for temporary visits outside
- Singapore Permanent Resident – Settled permanently in Singapore
- Foreigners – stay for 183 days or more for work/stay in the previous year.
Non Resident
All persons other than residents are treated as non-residents of Singapore.
Tax Rates
Singapore follows progressive income tax rates, that is, higher income attracts higher taxes. Slab rates are as follows
| Income Range (in Singapore $) | Tax Rate (in %) |
| 0-20000 | 0 |
| 20000-30000 | 2 |
| 30000-40000 | 3.5 |
| 40000-80000 | 7 |
| 80000-120000 | 11.5 |
| 120000-160000 | 15 |
| 160000-200000 | 18 |
| 200000-240000 | 19 |
| 240000-280000 | 19.5 |
| 280000-320000 | 20 |
| >320000 | 22 |
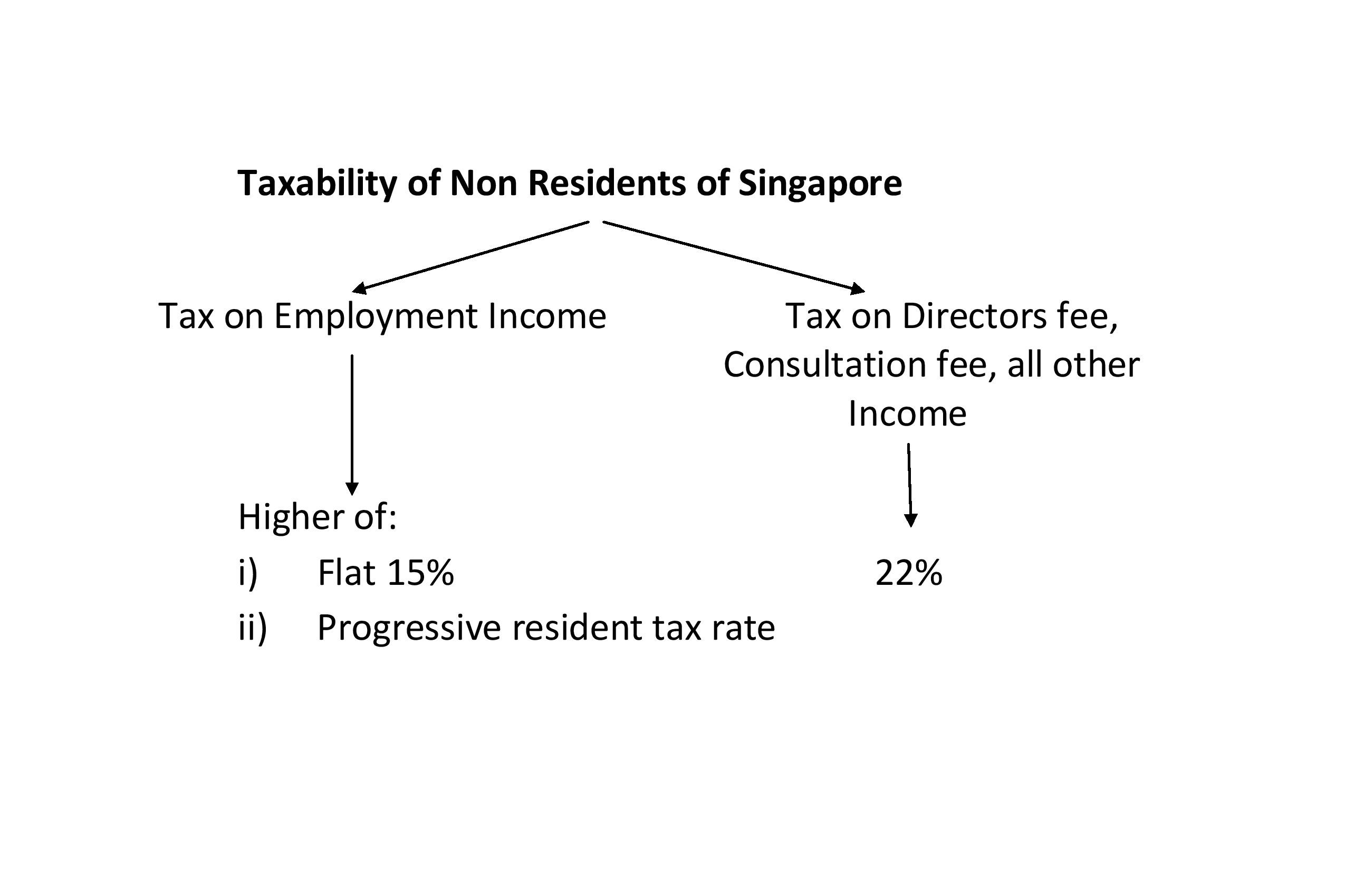
Non Resident
Due date of filing
It is mandatory for every individual to file its income tax returns by 15 April of every year to IRAS (Inland Revenue Authority of Singapore).

Corporate
Residential Status
A company is considered a resident of Singapore if it is controlled and managed from Singapore. Furthermore, controlled and managed means making decisions on the strategic matters, location of all the board meetings held, or the location of the person making key decisions of the company. Thus, even if the day-to-day operations are carried out in Singapore, a company will be considered as a non-resident if it is controlled and managed from outside Singapore. However, residential status from the point of view of income tax can change from year to year.
Tax Rates
Resident Companies
| Corporate Income (in Singapore $) | Tax Rate in % |
| Corporate Profits | 17 |
| Capital Gains by the company | 0 |
| Dividends distributed to shareholders | 0 |
| Foreign sourced income already taxed in other country | 0 |
Moreover, to promote new startups, new companies are given tax exemption for three years on the taxable income as follows:
- On first S$100000 – 75%
- On next S$100000 – 50%
If it meets the following conditions:
- The company must be a tax resident of Singapore
- It must be incorporated in Singapore
- The company should have not had more than 20 shareholders where all the shareholders are directly holding shares in their name
- The company must not have more than 20 shareholders where at least one shareholder is an individual who is directly holding at least 10% shares of the company.
However, certain companies are excluded from this benefit. They are:
- The company is engaged in the business of investment holding
- A company engaged in the business of development of a property, both either for sale or investment.
Non-resident companies
Non-residents are subject to withholding taxes on incomes like interest, royalty, fees for technical service, rental of property if they are deemed to arise in Singapore.
The due date for filing return
There are two types of filings with IRAS:
- ECI – Estimated Chargeable Income – It is to be filed within 3 months of the financial year-end.
- Form C or Form C-S – It is to be filed by November 30 if filed physically and by December 15, if filed electronically.
Income Tax in Dubai
As such, there is no personal income tax in Dubai. The short and sweet tax regime of Dubai is as follows:
| Particulars | Tax Rate |
| Tax on personal income | No tax |
| Corporate companies other than oil and gas companies and branches of foreign banks | No tax |
| Companies who are branches of foreign banks | 20% |
| Oil and Gas companies | Progressive rate up to a maximum of 55% |
| Income in AED (For Oil and Gas companies) | Tax rate in % |
| Upto 1L | 0 |
| 1L-2L | 10 |
| 2L-3L | 20 |
| 3L-4L | 30 |
| 4L-5L | 40 |
| >5L | 55 |
Income tax in India
Depending upon the person’s residential status, income tax in India is charged on the total taxable income of the person. Total taxable income is the gross total income less all the allowable deductions under Chapter VI-A.
Individual
Residential Status and Taxability
As per Income Tax Act, an individual is classified as Ordinary Resident, Non Ordinary Resident and Non Resident depending upon the number of stay days in India.
| Residential Status | Conditions | Taxability |
| Ordinary Resident (OR) | If one of the following two conditions is satisfied; Stay in India for 182 days or more in the year OR Stay in India for 730 days or more in immediately preceding 7 previous years | Global income is taxable in India |
| Non Ordinary Resident | If both of the following conditions are satisfied: I) Has been resident for at least 2 out of 10 immediately preceding previous years. II) Stay in India for 730 days or more in immediately preceding 7 previous years. | Only the income earned in India is taxable |
| Non-Resident | If none of the above two conditions are satisfied | Only the income earned in India is taxable |
Tax Rates for 2020-21
Due Date of filing returns
- Individuals whose accounts are not required to be audited – 31st July
- Individuals whose accounts are required to be audited/Partner of a partnership firm – 30th September.
Corporate
Residential Status
An Indian Company is always treated as a resident in India. Any other company would be considered a resident if its Place of Effective Management in India* is in India.
*Place of Effective Management (POEM): There could be many places of management but POEM will always be one. POEM is a place where key management and commercial decisions necessary for the conduct of business are made.
Taxability
With effect from A.Y. 2020-2021, there has been a change in the taxability of the companies. This can be better understood through the following table:
| Particulars | New Regime Tax rates |
| The company opts for section 115BAB. Not covered in section 115BA and 115BAA Registered on or after October 1, 2019. Commenced manufacturing on or before 31st March 2023. | 15% |
| The company opts for Section 115BAA. Total income of a company has been calculated without claiming specified deductions, incentives, exemptions, and additional depreciation. | 22% |
| The company opts for section 115BA. Registered on or after March 1, 2016, and engaged in the manufacture of any article or thing that does not claim the deduction as specified in the section clause. | 25% |
| Turnover or gross receipt of the company is less than Rs. 400 crore in the previous year 2018-19 | 25% |
| Any other domestic company | 30% |
Conclusion
Thus we see that there is a negligible tax in Dubai, comparatively higher in Singapore and highest in India. However, it is always advisable to seek professional opinion wherever required.
Join the LLA telegram group for frequent updates and documents.
Download the telegram group and search ‘Labour Law Advisor’ or follow the link – t.me/JoinLLA.
It’s FREE!



