Scams targeting people in India have become an alarming concern in recent years. These deceptive schemes, orchestrated by cunning individuals and organizations, have led to financial losses, emotional distress, and a pervasive distrust among the population. As the world’s second-most populous country, India offers a vast pool of potential victims, making it an attractive breeding ground for scam artists seeking to exploit unsuspecting individuals. This delves into the prevalent scams that have plagued the nation, examining the tactics used, the impact on victims, and the urgent need for heightened awareness and preventive measures.
Learn about five sophisticated scams and how to protect yourself from them in this “Jagruk Ban Na Hai.” Let’s discuss five advanced scams that individuals may fall victim to.
Table of Contents
1) Job scam
Job scams in India, like in many other parts of the world, are schemes designed to deceive individuals seeking employment. Scammers often exploit the desperation of job seekers, using various tactics to trick them into providing personal information, money, or both. Here are some common job scams and tips for spotting fake jobs:
1. Fake Job Portals:
- Scam: Fraudulent job portals may advertise non-existent jobs or redirect applicants to phishing websites.
- Tip: Use reputable job portals and verify the legitimacy of the website by checking for contact information, reviews, and the presence of a secure connection (https).
News: https://www.the420.in/delhi-police-busts-rs-1-crore-cyber-fraud-two-arrested/
2. Upfront Fees:
- Scam: Legitimate employers do not usually require payment from job seekers. Scammers may demand upfront fees for job placement, training, or other reasons.
- Tip: Be wary of any job that requires payment upfront. Research the company thoroughly and ask for detailed information about any fees.
3. Too Good to Be True Offers:
- Scam: Unrealistically high salaries, luxurious benefits, and minimal requirements could be signs of a scam.
- Tip: Research industry standards for the position and be skeptical of job offers that seem too good to be true.
4. Email and Phone Scams:
- Scam: Unsolicited job offers via email or phone that request personal information or immediate action.
- Tip: Verify the legitimacy of the offer by researching the company independently. Never provide personal information unless you are certain of the authenticity.
5. Fake Companies:
- Scam: Fraudsters may create fake companies with convincing websites to attract job seekers.
- Tip: Research the company’s background, contact information, and online presence. Legitimate companies typically have a history and online reviews.
6. Remote Job Scams:
- Scam: Scammers may offer remote jobs that require payment for training or equipment.
- Tip: Be cautious of remote jobs that require payment upfront. Legitimate remote jobs should not demand money from the employee.
7. No Clear Job Description:
- Scam: Vague job descriptions or promises of quick promotions with minimal effort.
- Tip: Legitimate job postings provide clear job responsibilities, qualifications, and expectations. Be skeptical of vague or overly positive descriptions.
8. Unprofessional Communication:
- Scam: Poorly written emails, job descriptions, or websites may indicate a scam.
- Tip: Legitimate employers maintain professional communication. Watch for grammatical errors, inconsistent language, or unprofessional design in emails and websites.
9. Lack of Company Information:
- Scam: Scammers may avoid providing detailed information about the company.
- Tip: Legitimate companies have a physical address, phone number, and a professional online presence. Verify this information before proceeding.
10. Pressure Tactics:
- Scam: Urgent requests for immediate action, such as signing contracts or making payments.
- Tip: Legitimate employers give candidates time to review job offers. Be cautious of high-pressure tactics that push for quick decisions.
Always trust your instincts and thoroughly research any job opportunity before committing. If something feels off, it’s essential to investigate further or seek advice from trusted sources. Additionally, reporting suspected scams to relevant authorities can help protect others from falling victim to similar schemes.
2) A job at a cost scam
It is a job scam where someone asks for payment upfront in exchange for a promised job. Job scams can take various forms, and it’s important to be cautious and aware of potential red flags. Here are some common signs of a job scam:
- Upfront Payment: Legitimate employers generally do not ask for payment from job seekers. If a job requires you to pay money upfront for training, materials, or any other reason, it’s likely a scam.
- Too Good to Be True: Be skeptical of job offers that promise high salaries or great benefits without requiring much effort or experience. If it sounds too good to be true, it probably is.
- Unprofessional Communication: Pay attention to the quality of communication from the employer. Legitimate companies typically communicate professionally. Poor grammar, spelling mistakes, or unprofessional email addresses can be red flags.
- No Clear Job Description: Scams may be vague about the job responsibilities or requirements. Legitimate job offers provide clear information about the position, including duties, qualifications, and expectations.
- Pressure to Act Quickly: Scammers often create a sense of urgency to pressure you into deciding without thoroughly researching or considering the offer. Be wary of employers who demand immediate action.
- Unusual Interview Process: Be cautious if the interview process seems unconventional or the employer is unwilling to conduct an in-person or video interview. Scammers may try to avoid direct interaction.
- Check the Company’s Reputation: Research the company online. Legitimate companies have an online presence, reviews, and information about their history. If you can’t find any information or the details seem suspicious, it could be a scam.
If you encounter a job offer that raises concerns, it’s advisable to trust your instincts and take the time to thoroughly research the company. Additionally, you can report suspicious job postings to relevant authorities or job platforms to help prevent others from falling victim to scams. Always be cautious and prioritize your safety when exploring job opportunities.
If you suspect that you have encountered a scam or fraudulent job offer, it’s crucial to take steps to protect yourself and report the incident. Here are some general tips on how to identify and avoid job scams:
- Research the Company:
- Check the company’s website, contact information, and physical address.
- Look for reviews and testimonials from current or former employees.
- Verify Job Offer Details:
- Be cautious of job offers that seem too good to be true.
- Verify the job details, such as job responsibilities, salary, and work hours.
- Communication:
- Be wary of job offers that require you to pay money upfront.
- Be cautious of job offers that only communicate through email or messaging apps.
- Interview Process:
- Legitimate companies typically conduct professional interviews, either in person or through video calls.
- Be cautious if the interview process seems unprofessional or irregular.
- Payment Requests:
- Legitimate employers do not usually ask for payment for job applications, interviews, or training.
- Be skeptical of requests for personal or financial information.
- Check for Red Flags:
- Spelling and grammar mistakes in job postings and emails can be a sign of a scam.
- Be cautious of job offers that come with a sense of urgency or pressure to accept quickly.
If you believe you have encountered a job scam, consider taking the following steps:
- Do Not Send Money: Do not send any money or personal information.
- Report the Incident: Report the scam to the relevant authorities or online platforms.
- Inform Others: Share your experience to raise awareness and prevent others from falling victim to the same scam.
- Contact Your Bank: If you’ve shared financial information, contact your bank to secure your accounts.
Always trust your instincts and, when in doubt, seek advice from friends, family, or professionals. Consider consulting with local law enforcement or a legal professional for guidance if you have specific concerns or details about a particular situation.
Be careful of the Bank KYC scam too. Sometimes, people pretending to be from your bank might call or text you saying you need to update your KYC info right away or your account will be frozen. They might send you a link to a fake bank website to steal your money. Remember, real bank employees won’t ask for your details like this. If you get a message about KYC, it’s best to talk to your bank directly.
3) Time to Renew
Scams involving “time to renew” calls are a common tactic used by fraudsters to trick individuals or businesses into providing sensitive information or making payments. These scams often target services like insurance, subscriptions, or memberships. Here’s how they typically work:
- Impersonation: Scammers may impersonate legitimate service providers, claiming to be from companies you have existing relationships with, such as insurance companies, utility providers, or software subscription services.
- Urgency: They create a sense of urgency, stating that it’s time to renew your policy, subscription, or membership immediately to avoid penalties, service interruptions, or other consequences.
- Verification: To “renew” your service, they may ask for personal information, such as credit card details, social security numbers, or account credentials, under the guise of verifying your identity.
- Payment: In some cases, scammers may request payment through unconventional methods, such as wire transfers or gift cards, making it difficult to trace and recover funds.
To protect yourself from such scams:
- Be Skeptical: If you receive an unsolicited call about renewing a service, be cautious. Legitimate companies usually send renewal notices by email or regular mail.
- Verify the Caller: Hang up and independently verify the contact information for the company claiming to call you. Use the official contact details provided on their website or official correspondence.
- Don’t Share Personal Information: Never provide sensitive information like Social Security numbers, credit card details, or passwords over the phone unless you initiated the call and are certain of the recipient’s identity.
- Check Your Accounts: Regularly monitor your bank and credit card statements for unauthorized transactions. If you notice anything suspicious, report it to your bank or financial institution immediately.
- Report the Scam: If you believe you have encountered a scam, report it to your local authorities and the relevant consumer protection agencies.
Remember, scammers use various tactics to exploit people, so staying informed and maintaining a healthy level of skepticism is crucial in protecting yourself from these types of scams.
4) Visa scam
Scams related to offering visas and other supporting documents for abroad visits and jobs are unfortunately common. It’s essential to be cautious and aware of potential red flags to avoid falling victim to such scams. Here are some common scams and warning signs:
- Unsolicited Emails or Messages: Scammers often send unsolicited emails or messages claiming to offer visa services or job opportunities abroad. Be wary of unexpected communication and research the legitimacy of the sender.
- Too Good to Be True Offers: If an offer seems too good to be true, it probably is. Scammers may promise high-paying jobs or quick and guaranteed visa approvals to lure victims.
- Request for Upfront Payments: Legitimate visa processes usually involve fees, but be cautious if you’re asked to pay large sums of money upfront. Scammers may request payment for visa processing, job placement, or other services that never materialize.
- No Physical Address or Legitimate Contact Information: Legitimate businesses and agencies have physical addresses and legitimate contact information. If the only way to contact the service provider is through a generic email or phone number, it could be a sign of a scam.
- Pressure Tactics: Scammers may use high-pressure tactics to rush you into making a decision. They might claim that the offer is time-sensitive to prevent you from thoroughly researching or thinking about the situation.
- Check the Website: Legitimate companies or agencies usually have professional websites with detailed information about their services. Be skeptical of poorly designed websites or those lacking comprehensive information.
- Inconsistent Information: Verify the information provided by the company or individual. Inconsistencies in details, such as names, addresses, or contact information, may indicate a scam.
- Research the Company or Agency: Before making any payments or providing personal information, research the company or agency offering the services. Look for reviews, testimonials, and other evidence of their legitimacy.
- Use Official Channels: When applying for visas or jobs abroad, use official channels such as embassy websites or reputable recruitment agencies. Avoid relying solely on third-party services that claim to expedite the process.
- Trust Your Instincts: If something feels off or too good to be true, trust your instincts. Take the time to investigate further before committing to any arrangement.
It’s crucial to stay informed and cautious when dealing with offers related to visas and job opportunities abroad. Always prioritize official channels and conduct thorough research before making any financial commitments. If in doubt, seek advice from trusted sources or authorities.
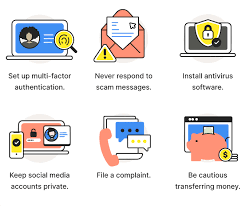
Awareness and Prevention
Awareness and prevention are critical aspects of protecting oneself from scams and fraud. They involve being well-informed about the various types of scams that exist, recognizing the signs of potential scams, and taking proactive steps to avoid falling victim to them. Here’s a more detailed explanation of the importance of awareness and prevention in the context of scams:
- Understanding the Types of Scams: Scams come in various forms, such as phishing emails, phone scams, investment fraud, identity theft, lottery scams, and more. Being aware of these different types of scams is the first step in protecting yourself. Each type of scam has unique characteristics and warning signs, so knowing what to look for is crucial.
- Recognizing Red Flags: Awareness involves recognizing red flags or warning signs that indicate a potential scam. These signs can include unsolicited communications, promises of quick and easy money, requests for personal or financial information, urgent or high-pressure tactics, and offers that seem too good to be true. Recognizing these red flags can help individuals avoid getting lured into a scam.
- Staying Informed: Staying informed means keeping up to date with the latest scam trends and tactics. Scammers constantly adapt and evolve their methods, so what was common in the past may not be the same today. By staying informed, you can learn about new scams and how to protect yourself from them.
- Educating Others: Awareness and prevention is not just for individuals but for communities and organizations as well. Educating others about scams and fraud is important, as it can help create a network of vigilant people who can share information and support one another in avoiding scams. This is especially important in the digital age, where scams can spread rapidly.
- Taking Preventative Measures: Prevention goes beyond awareness; it involves taking proactive steps to reduce the risk of falling victim to scams. This can include setting strong, unique passwords for online accounts, enabling two-factor authentication, regularly checking financial statements for unauthorized transactions, being cautious with personal information, and avoiding sharing sensitive information with unverified sources.
- Reporting Suspected Scams: If you encounter a potential scam or believe you have been targeted, reporting it to the relevant authorities or organizations is essential. This helps law enforcement and consumer protection agencies track and address scams while potentially preventing others from becoming victims.
- Seeking Professional Advice: In some cases, especially when dealing with complex financial or investment offers, seeking advice from a trusted financial advisor or legal professional can provide protection. They can help you navigate potential risks and ensure your financial decisions are sound.
Awareness and prevention are integral to safeguarding oneself from scams and fraud. By staying informed, recognizing warning signs, and taking proactive measures, individuals can significantly reduce their vulnerability to scams and protect their personal and financial information. In an interconnected world where scams are prevalent, a vigilant and informed approach is the best defense.
Financial Safety

Financial safety is a critical aspect of managing your money and protecting your assets. Scammers are constantly evolving their tactics to defraud individuals, so it’s essential to stay informed and take proactive measures to safeguard your finances. Here are some insights into scams targeting your finances and how to protect your money:
- Phishing Scams:
- Phishing scams involve fraudsters posing as legitimate entities, such as banks, government agencies, or trusted organizations, to trick you into revealing sensitive information like your login credentials, credit card details, or social security number.
- Safeguard your money by verifying the legitimacy of any communication. Always double-check the sender’s email address or website URL, and never click on suspicious links or download attachments from unknown sources.
- Identity Theft:
- Identity theft occurs when someone uses your personal information, such as your Social Security number, to open accounts, make purchases, or commit other fraudulent activities in your name.
- Protect your identity by regularly monitoring your credit reports, using strong, unique passwords for online accounts, and enabling two-factor authentication whenever possible.
- Investment Scams:
- Investment scams promise high returns with little risk and often target individuals looking to grow their wealth. These scams can take various forms, such as Ponzi schemes, pyramid schemes, or fraudulent cryptocurrency offerings.
- Safeguard your money by conducting thorough research before investing and consulting with a financial advisor. Be wary of any investment opportunity that seems too good to be true.
- Online Shopping Scams:
- Online shopping scams involve counterfeit products, non-delivery of purchased items, or fraudulent websites that aim to steal your credit card information.
- Protect your money by only shopping from reputable websites, checking for secure payment options (look for “https” in the URL), and reading reviews and ratings from other customers.
- Advance Fee Fraud:
- Advance fee fraud, also known as 419 scams, requires victims to pay a fee in advance to access a promised windfall or financial opportunity. Once the fee is paid, the scammer disappears.
- Protect your money by being skeptical of any request for upfront payments in exchange for a promised financial benefit. Legitimate opportunities typically don’t require you to pay money upfront.
- Tech Support Scams:
- Tech support scams involve scammers pretending to be from well-known tech companies and claiming your computer has a problem that requires their assistance.
- Safeguard your money by never giving remote access to your computer or sharing personal information with unsolicited callers. If you suspect a tech issue, contact the company directly through their official channels.
To safeguard your money effectively, it’s crucial to stay informed about the latest scams and continuously educate yourself on best practices for financial safety. Additionally, consider using antivirus software, identity theft protection services, and regularly monitoring your financial accounts for any suspicious activity. Always report any attempted or successful scams to the relevant authorities or organizations to help prevent others from falling victim to similar schemes.
Social Engineering
Social engineering is a term used to describe the manipulation of individuals or groups into divulging confidential information, providing access to restricted areas, or performing actions that may not be in their best interest. Unlike traditional hacking methods that focus on exploiting technical vulnerabilities, social engineering relies on psychological manipulation and trust to achieve its goals.
Here are some common types of social engineering scams:
- Phishing: In phishing attacks, attackers send emails or messages that appear to be from a trustworthy source, such as a bank or a legitimate organization. These messages often contain urgent requests for personal information, login credentials, or financial details. The goal is to trick the recipient into divulging sensitive information.
- Pretexting: In pretexting, the attacker creates a fabricated scenario or pretext to trick individuals into disclosing information or performing actions they wouldn’t normally do. This could involve impersonating a co-worker, IT support, or someone else in authority to gain access to sensitive data.
- Baiting: Baiting involves offering something enticing, like a free software download or a USB drive, with malware loaded onto it. When the unsuspecting victim takes the bait, they unknowingly compromise their system or network security.
- Quizzes and Surveys: Attackers might use seemingly harmless quizzes or surveys to collect information about individuals. People often share personal details willingly, thinking they are participating in harmless activities, but the collected information can be used for malicious purposes.
- Impersonation: This involves pretending to be someone else to gain trust. For example, an attacker might impersonate a colleague, a support technician, or even a friend to extract sensitive information or access secure areas.
- Watering Hole Attacks: In a watering hole attack, the attacker targets websites that the victim is likely to visit, such as social media platforms or industry forums. By compromising these sites, the attacker can infect the victim’s device with malware.
- Tailgating: This physical social engineering technique involves following someone into a restricted area without proper authorization. Attackers may pose as employees or contractors to gain entry to secure locations.
- Reverse Social Engineering: In reverse social engineering, the attacker presents themselves as a victim in need of assistance. They manipulate others into helping them by exploiting empathy and compassion.
To protect against social engineering attacks, individuals and organizations should be vigilant, verify requests for sensitive information, and educate themselves about common tactics used by attackers. Security awareness training, robust cybersecurity policies, and the use of multi-factor authentication can also help mitigate the risks associated with social engineering.
Online Threats

Online threats, including scams, phishing, and online fraud, pose significant risks to individuals, businesses, and organizations. These malicious activities leverage the anonymity and interconnected nature of the internet to exploit users for financial gain or to compromise sensitive information. Here’s an overview of some common online threats:
- Phishing:
- Definition: Phishing is a form of social engineering where attackers attempt to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information such as passwords, credit card numbers, or other personal details by posing as a trustworthy entity.
- Methods: Phishing often involves deceptive emails, messages, or websites that mimic legitimate ones. Attackers may use urgency, fear, or other emotional tactics to manipulate users into providing information.
- Online Fraud:
- Definition: Online fraud refers to any fraudulent activity that takes place on the internet to deceive users for financial gain. This can include identity theft, credit card fraud, and various scams.
- Methods: Fraudsters may use fake websites, deceptive emails, or malicious software to steal personal and financial information. Common examples include auction fraud, online shopping scams, and fake investment schemes.
- Malware Attacks:
- Definition: Malware, short for malicious software, encompasses a variety of harmful software types designed to disrupt, damage, or gain unauthorized access to computer systems. This includes viruses, ransomware, and spyware.
- Methods: Malware can be distributed through infected websites, email attachments, or compromised software. Once on a system, it can cause various damages, such as data theft, system disruption, or financial losses.
- Ransomware:
- Definition: Ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts a user’s files or entire system, rendering it inaccessible until a ransom is paid to the attacker.
- Methods: Ransomware is often delivered through malicious email attachments, infected websites, or compromised software. Once the files are encrypted, the victim is given instructions on how to pay the ransom to receive a decryption key.
- Social Engineering:
- Definition: Social engineering involves manipulating individuals into divulging confidential information or performing actions that may compromise security.
- Methods: Attackers may use psychological tactics, impersonation, or manipulation to exploit human behavior. This can occur through phone calls, emails, or other communication channels.
Protecting against these threats requires a combination of user awareness, secure online practices, and the use of cybersecurity tools such as antivirus software, firewalls, and secure browsing practices. Regularly updating software and being cautious about unsolicited communications can also help mitigate the risks associated with online threats.
Security Measures
Enhancing your online and offline security is crucial in today’s interconnected world where cyber threats and scams are prevalent. Here are some tips to help you protect yourself:
- Online Security
- Use Strong, Unique Passwords:
- Create complex passwords with a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Avoid using easily guessable information, such as birthdays or common words.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA):
- Enable 2FA wherever possible, especially for important accounts like email, banking, and social media.
- This adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second form of verification.
- Regularly Update Software:
- Keep your operating system, antivirus software, and applications up to date.
- Updates often include security patches that protect against the latest threats.
- Be Cautious with Emails:
- Avoid clicking on links or downloading attachments from unknown or suspicious emails.
- Verify the legitimacy of emails, especially those requesting sensitive information.
- Use a Secure Connection (HTTPS):
- Ensure websites use HTTPS to encrypt data in transit, especially when entering personal information or making online transactions.
- Ensure websites use HTTPS to encrypt data in transit, especially when entering personal information or making online transactions.
- Protect Personal Information:
- Be mindful of the information you share online, and adjust privacy settings on social media platforms.
- Avoid sharing sensitive information in public forums or unsecured websites.
- Regularly Back Up Data:
- Back up important data regularly to an external device or a secure cloud service.
- In case of a ransomware attack or hardware failure, you can restore your data.
- Offline Security
- Secure Physical Devices:
- Keep your devices physically secure, especially laptops, tablets, and smartphones.
- Use passwords, PINs, or biometric authentication to lock your devices.
- Shred Sensitive Documents:
- Shred documents containing sensitive information before disposing of them.
- This includes bank statements, medical records, and other personal documents.
- Be Wary of Phone Scams:
- Be cautious when receiving unsolicited calls asking for personal information.
- Verify the identity of the caller and never give out sensitive information over the phone.
- Check Your Credit Report:
- Regularly review your credit report for any unauthorized or suspicious activity.
- Report any discrepancies to the credit reporting agencies.
- Use Secure Wi-Fi Networks:
- Secure your home Wi-Fi with a strong password.
- Avoid using public Wi-Fi networks for sensitive transactions, or use a virtual private network (VPN).
- Educate Yourself:
- Stay informed about common scams and phishing techniques.
- Be skeptical of unexpected requests for money or personal information.
By implementing these security measures both online and offline, you can significantly reduce the risk of falling prey to scams and enhance your overall security posture. It’s essential to stay vigilant and adapt your security practices as technology and threats evolve.
Moreover, love scams have emerged as a heartbreaking deception, exploiting individuals seeking romantic connections. Victims are lured into fake relationships and manipulated into sending money, with scammers meticulously building trust over time. A shocking incident involved an IIT graduate losing Rs 57 lakhs to a scammer met through an online platform. This scam illustrates that no one, regardless of education or social standing, is immune to such deceit. Understanding the intricacies of love scams can help protect against financial loss and emotional trauma. Uncover the signs and prevention methods of love scams.
Lastly, it’s crucial to be aware of scams that exploit the powerful emotion of fear. Scammers often utilize fear as a weapon to manipulate individuals into acting against their best interest. The blog ‘Unveiling the Dark Art of Fear: 5 Unique Scams Exploiting Your Emotions‘ delves into various scenarios where scammers create a sense of urgency and panic to coerce victims into compliance. From threats of service disconnection in Electricity Bill Scam to fake legal actions in Data Entry Scams, understanding these tactics can equip you with the knowledge to stay one step ahead of fraudsters. Familiarize yourself with these emotional manipulation strategies to better safeguard your emotional and financial well-being.
If you’ve encountered or suspected a scam, it’s not only important to protect yourself but also to help prevent others from falling victim. Report any scams to the National Cyber Crime Reporting Portal. This official platform is a vital resource for combating cybercrime in India. Your report could be the key to stopping these fraudsters in their tracks.
To stay updated on the latest in scam prevention and online safety, subscribe to our newsletter, TSC (“The Success Circle“), at tsc.lla.in. Our newsletter provides timely legal insights, tips, and updates to keep you one step ahead of scammers. By staying informed, you can safeguard not only yourself but also your community from these digital threats.
Join us in the fight against scams and stay ahead in the digital safety game. Subscribe now!



