A partnership is a formal arrangement between two or more parties to manage and operate a business and share its profits. In this article of the Business Basics series, after covering Sole Proprietorship, we cover Partnership Firm. What is a partnership firm, how does one begin a partnership firm and what are the compliances involved. This article gives a breakdown of everything related to partnership firms.
Table of Contents
Formation of partnership firms
Who can become a partner?
Partnership firms are not restricted to individuals. Apart from individuals, different entities can also form a partnership firm. As long as an individual or enterprise has a legal entity, it can become a partner in a partnership firm. However, HUF cannot directly become a partner. It has to be represented by a separate entity.
How many partners can form a partnership firm?
Minimum two partners must be present. Furthermore, a non-banking firm can have maximum 20 partners. Whereas a banking firm can have maximum 10 partners.
How to decide the firm name?
A partnership firm can use any name, without any legal approval. Even if there are multiple other firms with the same name, there is no objection. Although it is not mandatory for a firm to suffix “and company” in its name, some partnership firms do it. However, suffixes such as “private limited” and “LLP” cannot be added to such firms on a whim. They can only be used for private limited and LLPs respectively.
How to make partnership deed?
The partners involved in the partnership firm can decide the rules and regulation to be followed themselves. This is called a partnership deed. It can have outlines regarding what kind of business the firm will do, segregation of capital each partner will introduce, division of profits of the firm, criteria to add new partners or remove existing ones, and likewise. There is no legal act to mandate the partnership deed. All parameters can be decided by the partners themselves.
A oral contract is sufficient for a partnership firm but to avoid legal hassles in the future a written contract called partnership deed is recommended.
Registered Vs unregistered partnership firm
There can be two types of partnership firms – registered and unregistered. If a firm is registered under the Registrar of Partnership Act then it is considered a registered partnership firm. Alternatively, if it not registered anywhere it is an unregistered partnership firm.
Furthermore, both registered and unregistered firms are undifferentiated under the Income Tax Act. Both are legal firms. It is not compulsory to register a partnership firm.

Documents required for registered firm
The identification proof of the partners involved, such as Aadhaar or PAN is required. Along with a notarized partnership deed is sufficient for registering a partnership firm.
Benefits of registering firm
- Registered partnership firm can file a case under their name against another entity. this is not possible for unregistered firms.
- Assets can be purchased under the partnership firm’s name only if it is registered.
PAN of partnership firm
Once a partnership firm is made and the partnership deed is made, the next important task is to apply for a firm PAN card. For the PAN application, individual partners’ identification and partnership deed will be required. This PAN will inform the Income Tax Department of the formation of the firm. It will then see the tax compliances of the firm as a separate entity from its partners.
Bank account for firm
The partners should open a bank account with the firm’s name. This will allow them to cash any check made under the firm’s name. To open the bank account, the partners’ PAN details, address proof and partnership deed will be required.
Capitalization of partnership firms
Adding capital
To start any work, a firm will require some capital. This capital can be introduced in the form of either cash or asset. It totally depends on the partners who choose what type of capital and how much capital to invest in the firm. Furthermore, there is no relation between the division of capital investment and profit-sharing in a partnership firm. All of these things depend completely on the partnership deed formed by the partners.
Getting loans
Moreover, any one of the partners can also give a loan to the partnership firm and claim interest on the loan. This feature is not available in a proprietorship firm. It is only possible in partnership firms. The loan can also be claimed for deduction under the partners ITR filing.
Silent partner
Partnership firms can also have silent partners. These are partners who will invest capital and receive profit division but will not be engaged in the day to day operations. The clauses applicable for the silent partner will be mentioned in the partnership deed.
Taking money out of partnership firms
There are some rules on how partners can take out money from a partnership firm for their usage, as follows:
- The partners can get up to 12% interest on the capital they invested in the firm. This interest will be added to their income and will be taxable.
- Partners can take a salary or remuneration or bonus or commission from the partnership firm. Income Tax Act, Section 40, Clause B states a formula for calculating this salary. According to this formula, the book profit of the partnership firm, i.e., net profit minus the interest paid to partners, will be calculated first. On the remaining profit, partners can receive 90% remuneration on up to Rs 3 lakh and 60% remuneration on above Rs 3 lakh.
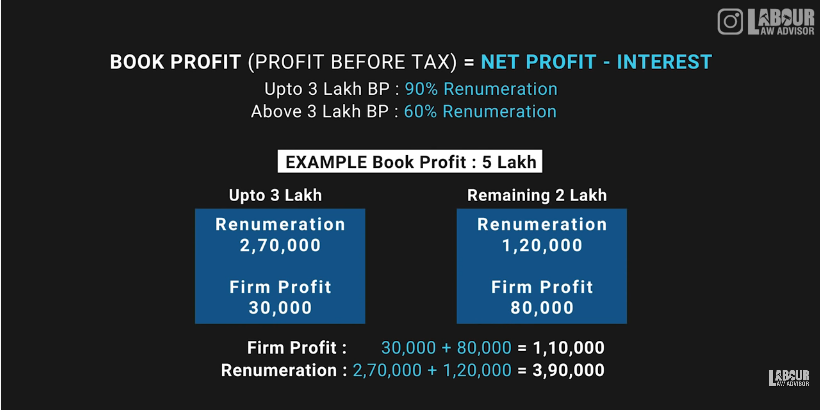
Profit sharing
On the remaining profit after interest and remuneration payments to partners, the firm has to 30% tax. Furthermore, the amount remaining even after tax payment can be reintroduced into the firm as capital or they can divided among the partners in the agreed profit sharing ratio.
This profit share is further exempt from taxes since the partnership firm has already paid taxes on it.

Altering partnership deed
In the course of a partnership firm, it is possible to edit the partnership deed as and when old partners leave, new partners join or division of profits change, etc. All of this is completely upon the understanding of the partners and how they want to function. They can edit the partnership deed when they need to.
Compliances for partnership firm
Following compliances are important to run a partnership firm:
- Shop and establishment act -applicable in all states.
- Professional tax – separately for partners as PTEC and for employees as PTRC. Applicable in some states.
- Labour welfare fund – applicable in some states.
- TDS – Tan number
- Income tax – annual return filing, advance tax
- Tax audit – if turnover exceeds Rs 1 crore
- GST – applicable for services firm if turnover exceeds Rs 20 lakh and for goods trading firm if turnover exceeds Rs 40 lakh. Otherwise, GST is not compulsory for smaller businesses.
- ESI and PF – as per the number of employees hired.
Dissolution of partnership firm
If the partnership firm is facing closure then it is important to give an intimation letter of closure to all departments where the partnership firm is registered. These may require some proof of closure.
Watch the video below on partnership firm business basics for further information.
Join the LLA telegram group for frequent updates and documents.
Download the telegram group and search ‘Labour Law Advisor’ or follow the link – t.me/JoinLLA
It’s FREE!



