All salaried employees get a salary slip from their employer periodically. A salary slip is a document which details the components of the salary that the employee is receiving and in what percentage. So it lists the basic salary, HRA, LTA, bonus as well as any deductions made such as for being late or absent. This document is generally given either physically or on mail to all employees. This article discusses the importance of salary slips, its components and other details.
Table of Contents
What is a salary slip?
A salary slip is essentially a legal document which serves as a proof of salary payment. It is given to the employee every month by the employer. It details the various components which the employer is paying the employee on a monthly basis. This will include components such as basic wages, HRA, LTA, bonus, etc. Additionally, it also details any deductions which employer is making on employee’s salary. This can be for PF, ESI, being late to office or unpaid leave, etc.
Benefits of salary slip
There are multiple benefits of receiving a salary slip as follows:
- Loan or credit card – When applying for any loan or credit card, one has to provide proof of income to the bank. The salary slip serves as proof in such cases.
- Term insurance – When applying for term insurance, a business person or professional needs to show their income tax returns for the past 3 years. However, a salaried employee needs to show their salary slip for the past few months and that is enough. Learn more about what is term insurance and how to get it in How to Select the Best Term Insurance Plan.
- Income tax calculation – Any person earning over Rs 5 lakh a year has to pay income tax to the government. Hence, salary slips serve an important purpose as one’s proof of income. They are also used to calculate the amount of income tax one has to pay.
- Visa application – When applying for a visa to visit a foreign country, one needs to procure their salary slip. This serves as proof that one has employment and social life in the native country and will not flee to the foreign country.
- Alimony ground – When discussing alimony in a divorce proceeding, the couple’s salary slips are discussed to see if and how much alimony one spouse will have to pay to the other.
- Increment proof – The salary slips also serve as proof for increment an employee receives during their tenure at a company. Furthermore, when joining a new company, the previous company’s salary slip may be asked for as proof of earlier employment.
Is salary slip mandatory?
As per the law, a wage slip and not salary slip is mandatory. There is a minor difference between wage and salary here. Technically, wages is given to unskilled workers in factories and labourers. Whereas salary is given to employees working in an office.
If salary slip is given physically then it needs to have the company stamp and signature. This is not necessary in digital slips though. According to labour laws, salary slip or wage slip must be given to all employees.
Salary components
CTC Vs Gross Salary Vs Net Salary
What is CTC?
CTC or Cost To Company is the expense that the company incurs upon hiring an employee. The CTC includes a number of variants such as – direct benefits (basic salary, dearness allowance, conveyance allowance, house rent allowance, medical allowance, leave travel allowance, vehicle allowance, telephone allowance, incentives/bonuses, special allowances), indirect benefits and savings contributions. CTC is a variable pay since it varies on many factors.
Legally, there is no mention of CTC in any labour law. It is a term manufactured by HRs which has made its way to the offer letter nowadays. So while CTC maybe a big amount, the actual cost in hand which employee receives maybe very less.
What is gross salary?
Gross salary is the EPF and Gratuity deducted from the CTC. Thus, gross salary is the amount the employee receives before the deduction of taxes. Gross salary is also inclusive of holiday pay, overtime pay, bonuses and other differentials.
What is net salary?
Net salary or in-hand salary is the actual salary which the employee receives in-hand, after tax and other deductions. This includes deductions for TDS and other company policies.
To learn how to calculate your salary read CTC Vs Gross Vs In-Hand Salary | Understanding The Hierarchy.

Rate Vs Earned Vs Arrear
Rate is the parameter mentioned on the offer letter of an employee. This stands for the rate of different salary components which the employee is supposed to receive.
Earned is the amount of the salary components the employee should receive as per the number of paydays they have. Hence, depending on the number of days an employee has been present at work, he will receive his earned salary. Therefore, earned salary can be either less or at the most same as the rate of salary.
Arrear is any pending salary component which was not paid earlier and is being paid later.
TDS Vs Income tax
The government has mandated companies to deduct TDS on salaries of employees with high earnings. This is to ensure that the employee does not relent from paying their taxes in a way.
On the other hand, income tax is the actual amount of tax one has to pay annually as per all their earnings and investments. It can happen, that the employer may deduct more TDS than employee’s actual income tax amount. In that case, employee will receive TDS refund. Alternately, employer may also deduct less TDS than actual income tax amount. Then employee has to pay the remaining amount to government in taxes.
Hence, income tax has to be paid by the employee. While TDS is deducted and paid by the employer separately. Finally when filing ITR, employee has to check for any mismatch in the income tax and TDS calculations and refund or pay the remainder amount.
Learn about TDS calculation in salary in How To Calculate TDS And Reduce TDS On Salary. Also, learn about ITR filing for checking TDS in TDS Refund Filing Online Procedure.
Exemptions Vs Deductions
What are exemptions?
Chapter 3 of the Income Tax Act of 1961 states the provision of income tax exemption. There are certain types of income sources on which you can get an exemption from tax payment. Hence, these sources of income are not added to the income tax calculation process. Thus, Exempted Income refers to some sources of expenditure, income or investment on which no tax payment is levied, thus reducing the overall taxable income. Some examples of Exempted Incomes are as follows:
- House Rent Allowance or HRA. Learn full information on this topic in our blog, House Rent Allowance (HRA) | Calculation & Exemption Rules.
- Leave Travel Allowance or LTA. Learn more details about LTA in our blog, Leave Travel Allowance (LTA) | How To Claim Income Tax Deduction?
- Any Gratuity or VRS or Pension which one receives in the assessment year. Learn more about Gratuity in our blog, Gratuity Calculation Formula | How much gratuity money will I get?
- Monies received as perquisites such as cellphones, lapops, etc.
- Accommodation from the employer.
- Agriculture income
- Profit from a partnership firm.
- Children Education Allowance and Hostel Allowance. Learn more in our blog, Children Education Allowance & Hostel Allowance | Tax-Saving Tips
What are deductions?
A Tax Deduction is a deduction from a person’s Taxable Income which thus reduces their tax liability. Tax deductions are usually expenses which the taxpayer incurs during the financial year. These deductions are then subtracted from the taxable income to figure the actual tax liability of a person. Following are some of the types of tax deductions applicable:
- Public Provident Fund. Learn more, PPF Scheme – Details & Benefits Explained.
- Life Insurance Premium
- National Saving Certificate
- Bank Fixed Deposit
- Senior Citizens Savings scheme. Learn more, Senior Citizens Savings Scheme (SCSS) Investment.
- Post office time deposit
- Unit-linked insurance plans
- Home loan EMIs
- Mutual funds and ELSS. Learn more, Types Of Equity Funds Available In Market.
- Stamp duty and registration charges for a home
- Retirement savings plan
- Tuition fees
- Medical insurance premiums
- Infrastructure bonds
- Charitable contribution
- Treatment of disabled dependents
- Deduction for preventive health check-ups
- Interest aid on education loan
- Deduction on house rent paid
Learn more about exemptions and deductions in Income Tax Calculation, Slab Rates & Important Details For Beginners.
Format of salary slip
A standard format of a salary slip contains the following components:
- Employee details
- Income/ reimbursement details
- Deductions details
- Bank details/ Net pay
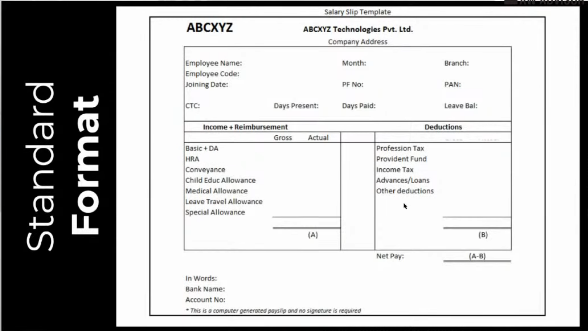
Components of salary slip
Employee’s personal information
- Employee’s full name
- Father/ husband’s name
- Residential address
- Designation in company
- Employee code
- Grade and rank if any
- Mode of payment – cash/cheque/bank transfer
- Details of payment
Attendance information
- Present days
- Rest days
- Paid leaves – SL/CL/EL
- Holidays
- Leave balance
- Overtime hours
- Total paid days
Learn more about attendance information in Paid Leave Calculation | How Many Earned Leaves As Per Law?
Learn about attendance calculation in How To Make Automated Attendance Sheet In Excel? | Attendance Register As Per Labour Laws.
Earnings
- Rate and earned
- Basic salary
- Allowances
- Dearness allowance
- Housing rent allowance
- Transport/ Conveyance allowance
- Medical allowance
- Leave travel allowance
- Special allowance
- Payment for overtime work
- Ex gratia
- Performance or sales incentive/ Bonus
- Gross earned
Deductions
- Tax deductions
- Social security/PF
- Workplace/ group accident cover
- Medical and healthcare insurance
- Advance payment/ adjustments on loans
Salary slip example
Example 1
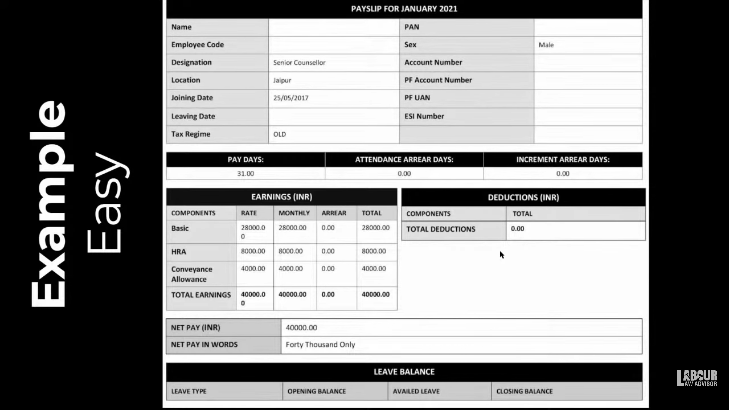
In example 1 given above, Earnings has 3 components – basic, HRA and conveyance allowance. There are also no deductions. There are no arrears as well. This is a simple and easy to understand salary slip.
Example 2
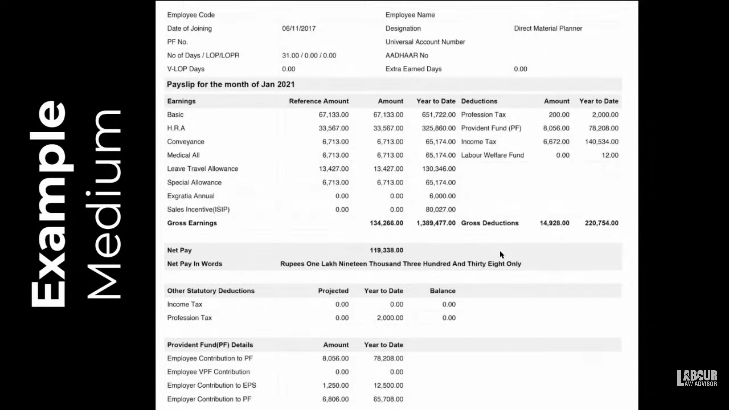
Now in example 2 above, the earnings have been randomly divided into components. There is no proper division of the components. It is just taken as fixed percentage of the basic and allotted without actually thinking if it is viable.
The deductions show the taxes and social security deductions made from employee’s salary. Additionally, the bottom part shows the breakdown of the social security payment.
Example 3
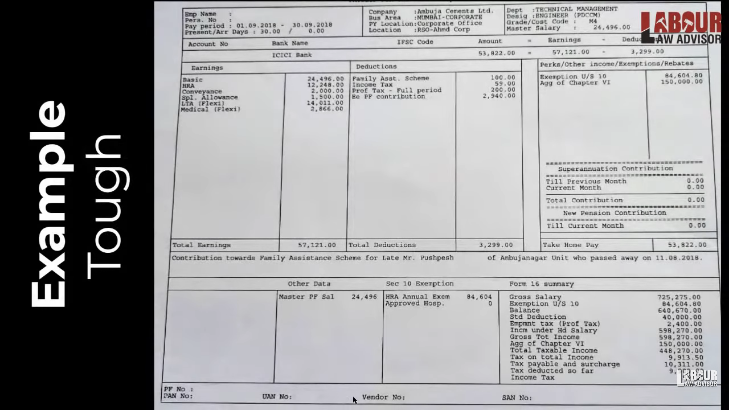
The example 3 above is an extremely complex one. It lists multiple and in some cases unnecessary components of earnings and deductions which may require professional accountant help to decipher.
Impact of Code on Wages
The Code on Wages Bill was introduced in March 2015 as a Draft of Labour Code first. It was later put out for public discussion for 30 days. After some initial changes, it was reintroduced at the Second Tripartite meeting in April 2015. It was the first presented in the Lok Sabha on August 2017 but it passed on to the Parliamentary Standing Committee. In December 2018, the standing committee submitted its report but due to the dissolution of the Lok Sabha, the bill lapsed. In July 2019, the bill was reintroduced under a new name, Code on Wages Bill. It was passed by both the Lok Sabha and the Rajya Sabha consecutively.
According to the Code on Wage, if the sum of the components in the exclusion is more than 50% of the remuneration being given by the company then the excess part will be added to employee’s wages. Thus, the basic and DA can never exceed 50% of the overall remuneration.
Learn more about Code on Wages in Code On Wages Bill, 2019 | Complete Analysis and What Are The 4 Labour Codes? | Analysis & Status Update.
Watch the video below for more details.
Join the LLA telegram group for frequent updates and documents.
Download the telegram group and search ‘Labour Law Advisor’ or follow the link – t.me/JoinLLA
It’s FREE!



